
Two of the orbitals contain lone pairs of electrons.

The shape of the orbitals is tetrahedral. The molecule that is made up of 4 equally spaced sp3 hybrid orbitals forming bond angles of approximately 109.5o. These compounds are also called cyclic.īent Molecular Geometry The most common ring compounds contain either 5 or 6 carbons. The simplest ring compound contains 3 carbons as in cyclopropane.
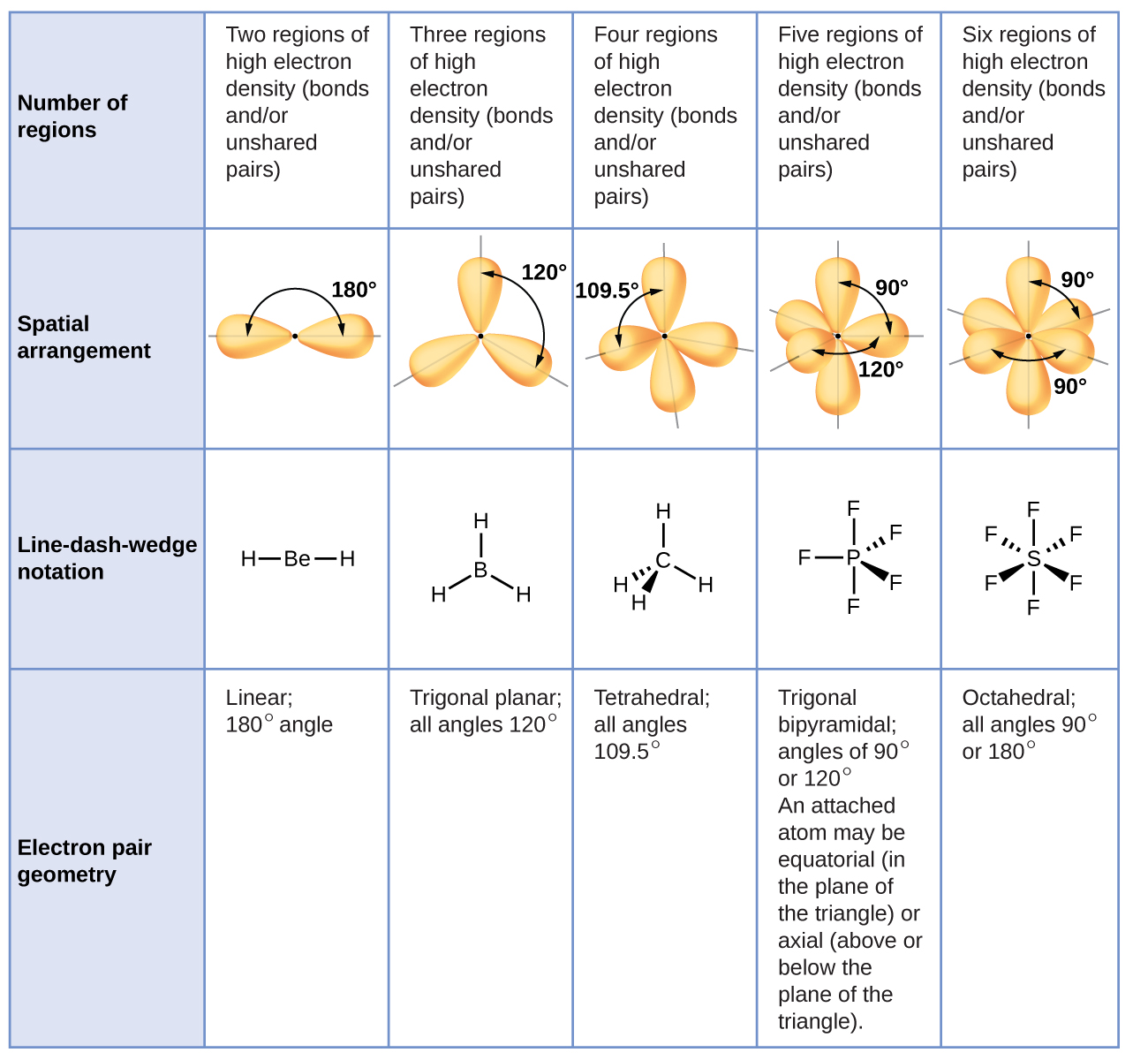
Many organic compounds contain rings of carbon atoms or other atoms such as oxygen or nitrogen. These are just a few of the basic postulates of the VSEPR theory that, along with the lewis dot structure of a molecule, allow us to determine the shape it will have. In this case an extra step is needed to to translate from electron pair geometry to the final molecular geometry, since only the positions of bonded atoms are considered in molecular geometry.ġ) The electron pairs and atoms around a central atom will give a molecule its shape.Ģ) Electron pairs around a central atom in a molecule will attempt to be as far away from each other as possible.ģ) Lone pairs around the central atom will have an effect on the shape of the entire molecule, just like an atom would.Ĥ) Lone pairs of electrons repel each other more strongly than a lone pair and a shared pair, which in turn repel each other more than two shared pairs (or bonds between the central atom and another atom). Group 2: Molecules with one or more lone electron pairs. In this case the molecular geometry is identical to the electron pair geometry. Group 1: Molecules with NO lone electron pairs.

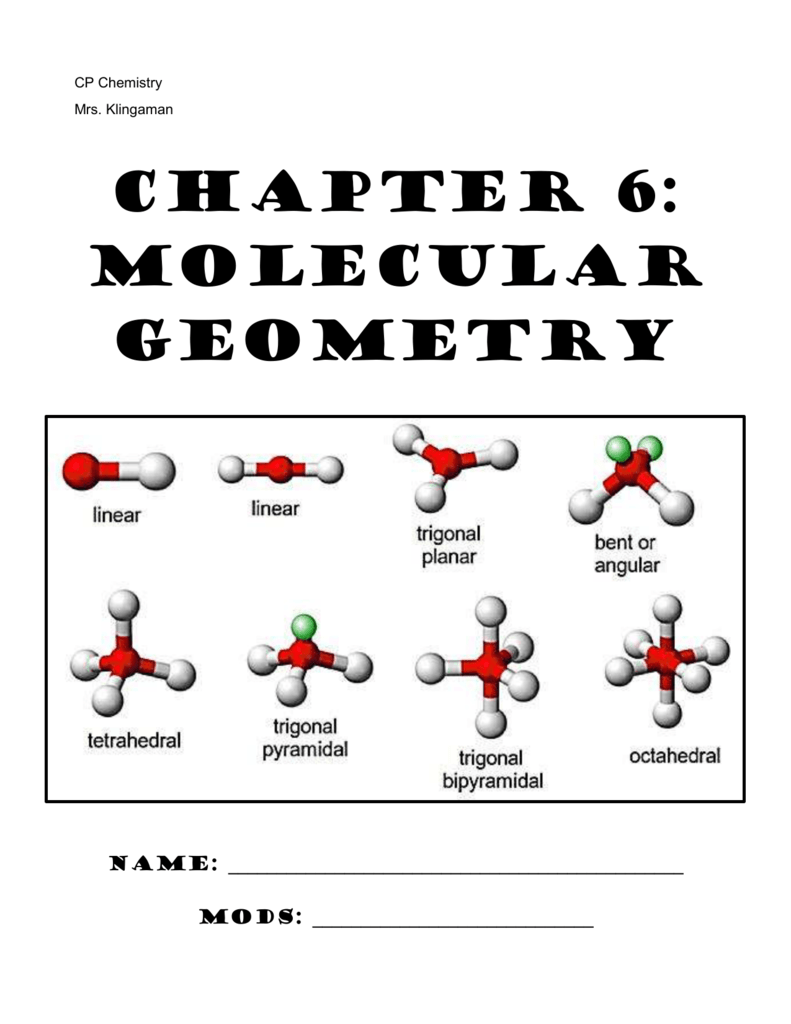
Molecules can then be divided into two groups: With this model in mind, the molecular geometry can be determined in a systematic way. This model produces good agreement with experimental determinations for simple molecules. According to VSEPR theory, molecular geometry can be predicted by starting with the electron pair geometry about the central atom and adding atoms to some or all of the electron pairs. The balloons will try to minimize the crowding and will spread as far apart as possible. Each balloon represents an electron pair. The idea of "electron pair repulsion can be demonstrated by tying several inflated balloons together at their necks. The repulsion between negatively charged electron pairs in bonds or as lone pairs causes them to spread apart as much as possible. In a polyatomic molecule, several atoms are bonded to a central atom using two or more electron pairs. In a covalent bond, a pair of electrons is shared between two atoms. The valence shell is the outermost electron-occupied shell of an atom that holds the electrons involved in bonding. Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theoryĮlectron pairs around a central atom arrange themselves so that they can be as far apart as possible from each other. Some of the most common shapes that can be taken are linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, pyramidal, and angular (or bent). This method states a few rules to help one determine the shape of a substance without using high technology methods such as X-ray crystallography, NMR Spectroscopy, or electron microscopy. The shape of most molecules can be predicted using the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) method. It is determined by the central atom and the surrounding atoms and electron pairs. Molecular geometry is the 3-dimensional shape that a molecule occupies in space.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
